Among athletes, Achilles tendon pain is often the consequence of training errors. Load induced pain with swelling and tenderness of the tendon are common features . Achilles tendon pain in the mid-portion of the Achilles tendon is located 2-6 centimetres apart the calcaneal insertion and should be differentiated from retro calcaneal bursitis and insertional Achilles tendon. Ultrasound with both greyscale and colour Doppler versions will help determine the degree of structural deterioration of a given tendon stop magnetic resonance imaging can add further details on structural abnormalities. Shockwaves in Achilles tendon puffy is a valid option, both as a single therapeutic means or, even better in combination with modalities such as eccentric training. Both focus and radial shockwaves can be effective in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy.
As the thickest tendon in the body, the Achilles tendon is a common sight for overuse injuries. Sports such as running and ball sports which involve running (e.g. football and handball ) place high loads on the Achilles tendon. Rapid acceleration, changes of direction high-speed and jumps can facilitate the development of Achilles tendon pain. Overuse injuries are often described as being like an iceberg – asymptomatic minor damage is hidden below the surface and proceeds these symptomatic tendon problems
Diagnosis
load -dependent pain is the main clinical symptom of Achilles tendon injuries, initially pain is only experienced after loading stage II when running is painful, but the pain does not stop the athlete from competing his training stop when Achilles tendon problems progress, the athlete is unable to complete his training and is forced to stop due to Achilles tendon pain. Finally stage IV is characterised by Achilles tendon pain even at rest stop
in addition to load induced pain in the course of normal daily activities, many patients with Achilles tendinopathy complain of pain when executing the first steps in the morning. The duration of this early morning pain can also be used to measure the current severity. This early morning pain can last for a few steps, a few minutes, or a few hours and it can also occur after prolonged sitting, for example when travelling all at a theatre
Swelling of the Achilles tendon usually indicates Achilles tendinopathy,
the site of maximum pain can and should be determined to allow the clinical classification as follows
- Mid-portion tendinopathy to to 7 cm above the insertion of the Achilles tendon into the heel
- Retro calcaneal bursitis the posterior aspect of the protrude rents found in Haglund`s deformity is covered by the retro calcaneal bursa. Can lead to pressure induced pain and damage (impingement lesion close paragraph to the Achilles tendon at this point.
- Insertional tendinopathy at the insertion of Achilles tendon into the calcaneus, which can also be accompanied by a posterior heel spur, calcaneal bone marrow oedema and affect the sharpie’s fibres.
Response rates to various treatments also differ from insertional symptoms in comparison with mid-portion ones will stop in mid-portion is Achilles tendon opposite, pure eccentric training uses the Alfredsson protocol achieved good results in 89% after 12 weeks, but with insertional problems only 32% had a good response to the same training regime. Since insertional tendinopathy affects both the bone and the tendon, extracorporeal shockwave can, in principle also produce a sustained improvement in the calcaneal bone marrow oedema as well as the tendon component.
Histology
histological examination of tendinopathic Achilles tendon is show the following changes compared with healthy Achilles tendons
- An increased ratio of collagen III
- buckling of the collagen articles in the extracellular matrix
- buckling of Tenocytes
- an increase in the ratio of small diameter collagen fibrils
Microcirculation alterations in painful Achilles Tendons
in 2006, we identified significant differences between the microcirculation of the painful site and the remainder of the Achilles tendon in patients with mid-portion and insertional tendinopathy. Capillary blood flow at the pain site was significantly increased with blood flow in the surrounding tendon. We also found that eccentric strength training was able to reduce this ink creased capillaries blood flow by 30 to 50% after 12 weeks. Gender differences were also reflected in microcirculation, with symptomatic women showing better tissue oxygenation and men, whereby the increase in blood flow was comparable
The neovascularisation can be viewed as a symptom of failure of Achilles tendon to heal. Miss loading (over – or under loading) thereby results in a persistent inflammatory neovascularisation. Painful Achilles tendon’s exhibit pathologically increased capillary blood flow at rest and this can be visualised using Power Doppler ultrasound.
Identification of neovascularisation with Power Doppler ultrasound is a significant risk factor for runners and can be used to screen at risk athletes. And analysts of 634 runners with no Achilles tendon symptoms found that the presence of neovascularisation statistically was a highly significant predictor of Achilles tendon problems, with a relative risk of 6.9 of experience Achilles tendon pain within one year stop the previous history of Achilles tendon problems was associated with a relative risk of 3.8
the new vessels produced during neovascularisation are closely associated with nerve fibres carrying pain mediators such as P substance neurokinin-1 receptors glutamate receptors catecholamines and cholinergic receptors such as Alpha 7
biomechanical compliance of the Achilles tendon’s also decreases with age, soneestastogrphy shows that the Achilles tendon is with insertional tendinopathy have a lower elasticity.
Treating Achilles tendinopathy
the choice of treatments in general depends on the clinical presentation the severity of the symptoms, how long the patient has had the symptoms, on the previous failed attempts at treatment, the level of sporting achievement, the patient is hoping to obtain, and the patient’s level of compliance (with respect to eccentric strength training for example) at the elite level, the focus is on the time until the patient can return to training and competition. In most therapists experiences combined Multimodal approaches incorporating shockwave can be highly beneficial.
Radial and/or focused shockwave procedures can be used to treat Achilles tendinopathy. In Germany shockwave is traditionally administered over 3 to 5 sessions at intervals of 1 to 5 weeks, elite athletes this may vary in isolated cases and depending on the map situation sometimes they can administer focused and radial shockwave sessions daily but this is not a recognised procedure and there is no data published so far
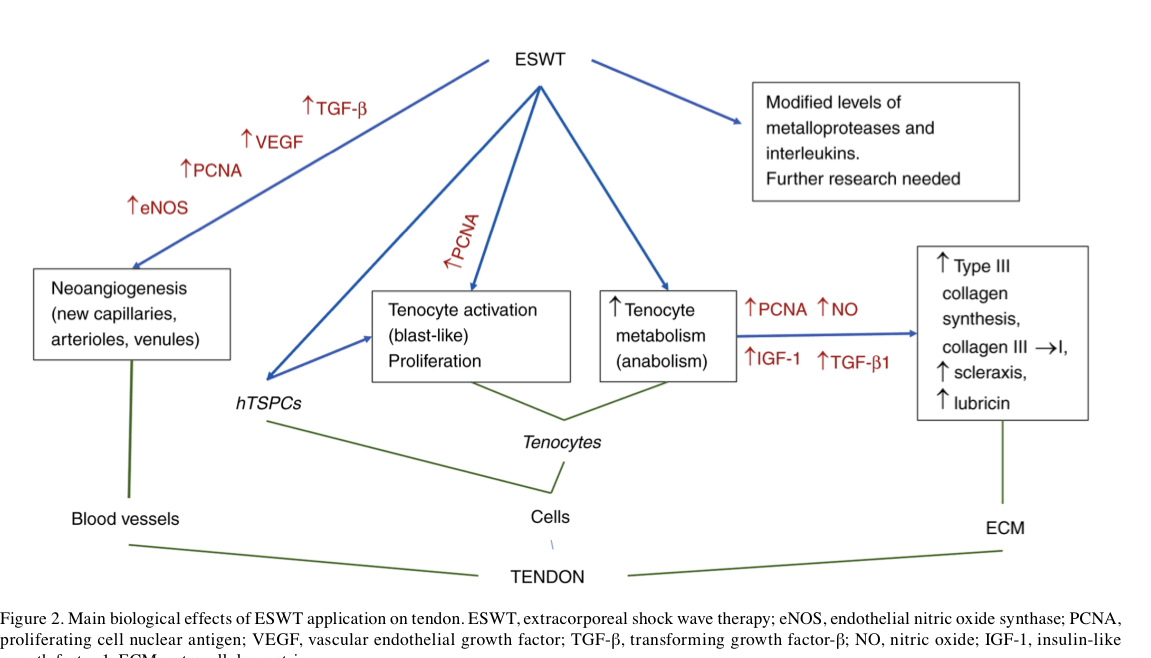
Relevant studies generally look at outcomes 3 to 6 months after completing the shockwave. It is likely that the clinical variability affects (power pain reduction, reduction in swelling, and where application is a reduction in swelling, close paragraph can also be observed before the three-month period has elapsed the underlying mechanism of shockwave action in Achilles tendon opposite includes activation of tendon stem cells
Achilles tendon problems are often accompanied by clinical identification trigger points in the medial and lateral gastrocnemius these can be treated with a combination of radial and focused shockwaves
 Here you can listen to the excellent pod cast by Dr Carlo de Miao click here
Here you can listen to the excellent pod cast by Dr Carlo de Miao click here
SOME OF THE PAPERS
Vahdatpour(2018)- SWT on Achilles Tendinopathy – RCT